Why Should Your Brokerage Offer PAMM and MAM Accounts to Clients?
 By Hazem Alhalabi
By Hazem AlhalabiA versatile writer in a wide range of concepts, specifically in Web3, FinTech, crypto and more contemporary topics. I am dedicated to creating engaging content for various audiences, coming from my passion to learn and share my knowledge. I strive to learn every day and aim to demystify complex concepts into understandable content that everyone can benefit from.
Long hours of reading and writing are my bread and butter, and my curiosity is the catalyst to becoming the experienced writer I am. I excel at writing in English and Arabic languages, and I am endlessly looking to explore new realms and endeavours.
 By Tamta Suladze
By Tamta SuladzeTamta is a content writer based in Georgia with five years of experience covering global financial and crypto markets for news outlets, blockchain companies, and crypto businesses. With a background in higher education and a personal interest in crypto investing, she specializes in breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand information for new crypto investors. Tamta's writing is both professional and relatable, ensuring her readers gain valuable insight and knowledge.

Operating a brokerage company entails dealing with traders’ accounts and funds, offering trading services and options to grow their wealth. PAMM and MAM accounts are two money management systems that allow traders to diversify their portfolios and explore various options to increase their income.
Brokerage firms offer one or both MAM and PAMM trading, adding flexibility to trading accounts by assigning managers to deal with the investors’ money.
Let’s discuss the difference between these managed account types and why you should offer them to your clients.
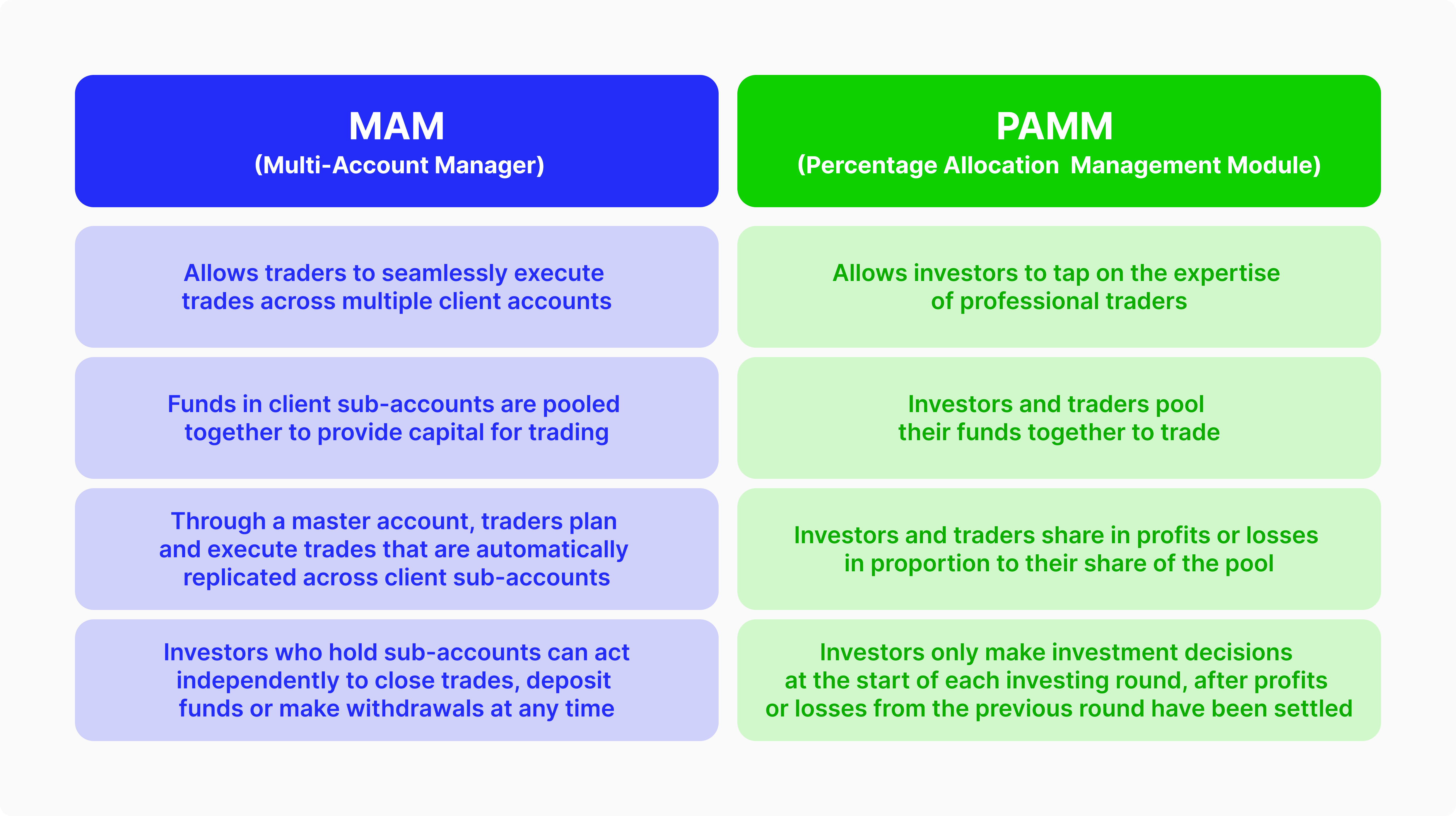
PAMM and MAM accounts are two types of managed trading accounts where users invest in the market utilising the knowledge and experience of professional money managers.
PAMM accounts work by traders and managers pooling their funds together and managers executing trades, sharing profits and losses proportionally.
MAM accounts are created by traders who connect subaccounts to a chosen expert’s master account. Each trade in the master account is reflected in the sub-accounts.
MAM trading accounts are more flexible and offer more customisation for traders than PAMM Forex trading accounts.
PAMM and MAM, or percentage allocation money management and multi-account manager, refer to investment models that include entrusting a money manager to manage multiple accounts and trade on behalf of the user.
Despite the similarities between these two accounts, they follow different systems for allocating and managing funds. Moreover, their profit distribution and contributions are planned differently.
MAM and PAMM account providers enable traders to utilise account managers’ expertise and market knowledge. Additionally, they offer freedom, especially for investors who cannot dedicate all their time to trading activities or have limited experience.
If you are running a Forex brokerage firm, offering PAMM and MAM accounts is a great idea to onboard more clients, specifically those looking to diversify their investments.
Also, these accounts usually involve wealthy individuals and high-end institutional investors, which makes it a lucrative business, capitalising on earnings and percentages accumulated from their deposits and gains.
With the development of electronic trading platforms, PAMM and MAM accounts grew in popularity, offering users different models to increase their wealth besides the regulator order execution function.
Traders can seamlessly explore multiple money management systems in the trading software, selecting the suitable strategy that suits their preferences and objectives.
These trading systems include a trader acting as a money manager, who traders for themselves and on behalf of other investors, who entrust the manager with their funds. Investors may choose the appropriate Forex money manager based on their years of experience and market, such as FX, stocks, etc.
Therefore, by offering these accounts, it is crucial to incorporate transparency and security measures, ensuring the investors’ funds are not exposed to bad actors or unexpected risks.
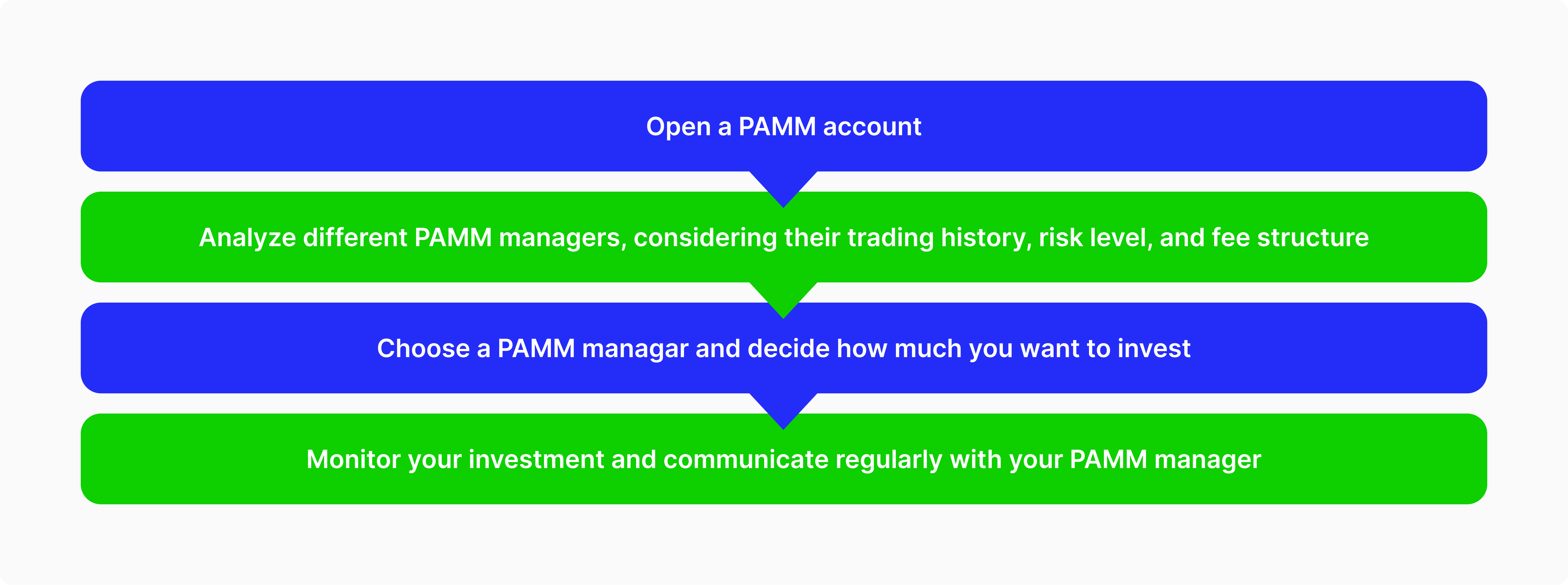
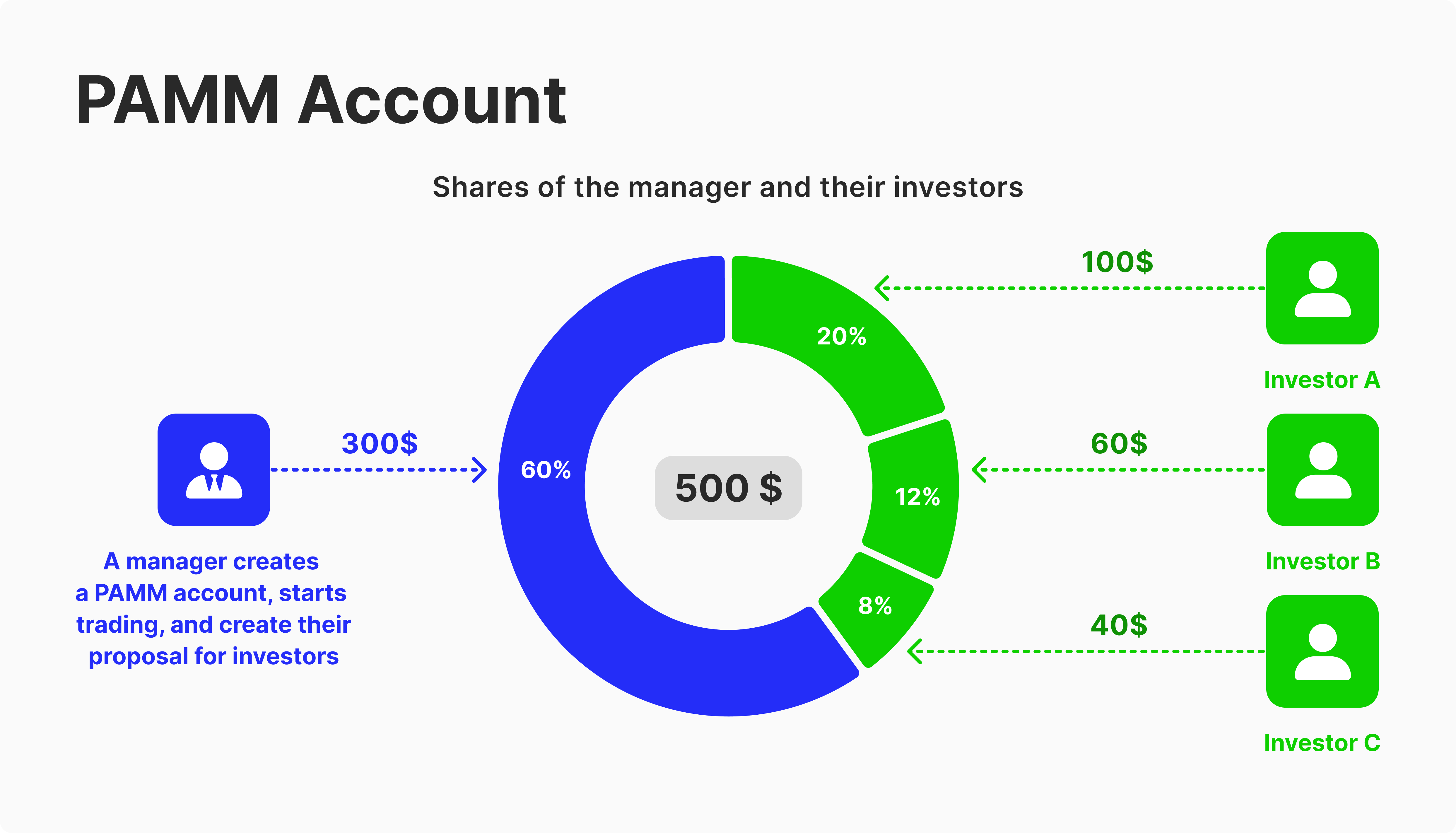
A PAMM account, short for percentage allocation money management, is a money management system where traders deposit their funds together in one pool and choose a money manager to make trading decisions using the whole pool.
Traders designate a money manager according to their portfolio, success rate, profits record, risk management style, and more to have the most profitable PAMM account.
However, not every trader can become a money manager, as brokerage companies conduct a comprehensive screening and evaluation to assign proficient fund managers with a proven track record and history.
Gains and losses of the PAMM account are distributed between participant traders, each according to their contribution as a percentage of the entire pool.
Before signing up for a PAMM trading account, participants enter into a limited power of attorney agreement with the money manager. This gives them the right to make investment decisions on traders’ behalf and realise the risk associated with trading.
The agreement, supervised by the PAMM account provider, states the amount each FX trader has deposited and the commission fees charged for this service.
Let’s explain how PAMM accounts work through the following example. Assume Jack, John and James are three Forex traders who want to invest in a PAMM account, and they choose Mark to be their account money manager.
Each trader, including Mark, makes their contribution as the following:
Jack = $2,500 (16.6%)
John = $3,500 (23.4%)
James = $4,000 (26.6%)
Mark = $5,000 (33.4%)
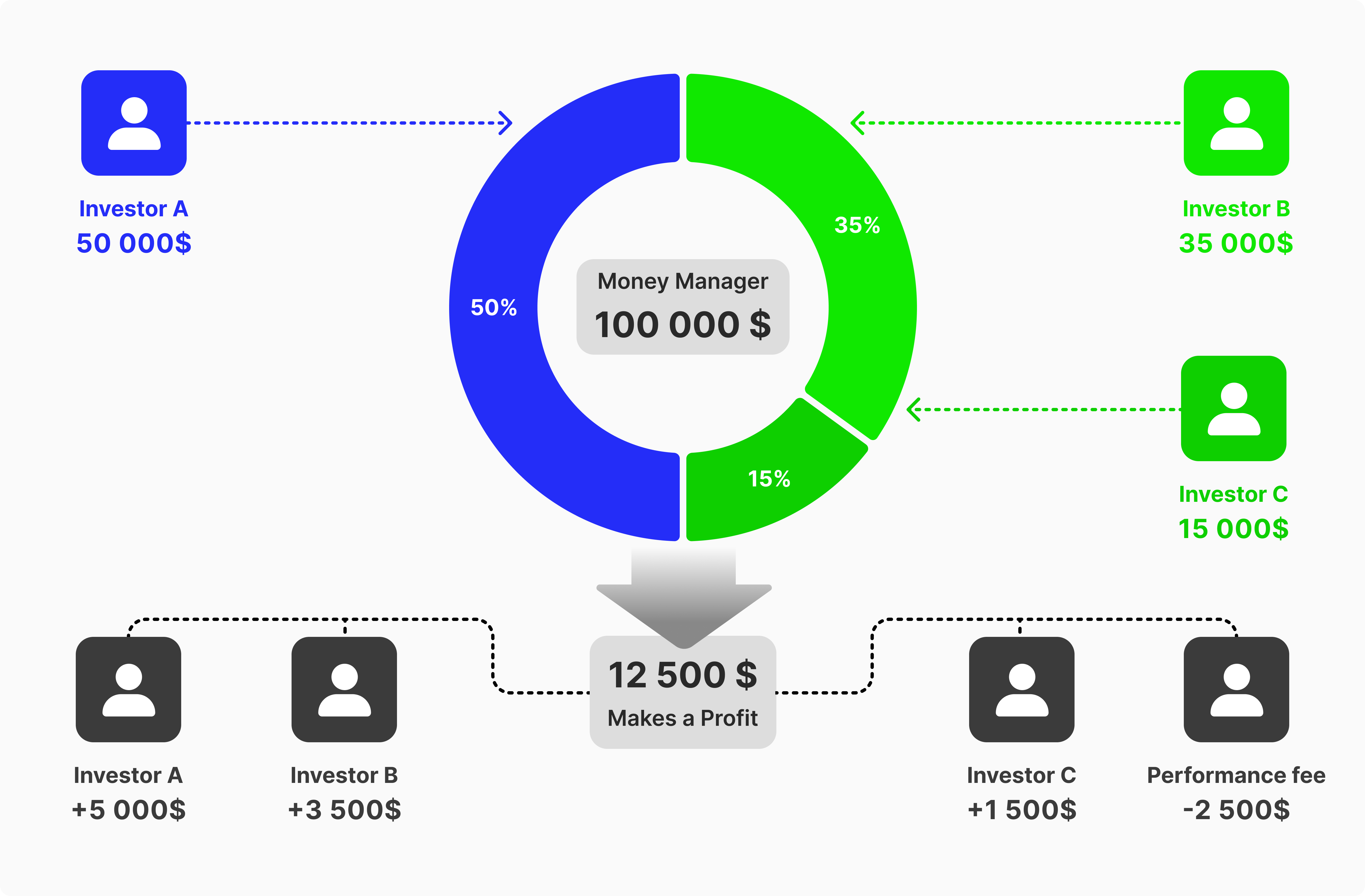
After a couple of weeks, Mark managed to land some successful trades, growing the funded pool by 30%. The total funds now equal to $19,500 (30% * 15,000).
The accumulated profit of $4,500 is then distributed proportionally to the four participants. However, Mark charges a 10% fee for his services, which equals $450.
The resulting $4,050 is allocated to each investor by multiplying the total profit by the contribute percentage, as follows.
Jack = $4,050 * 16.6% = $675
John = $4,050 * 23.4% = $945
James = $4,050 * 26.6% = $1,080
Mark = $4,050 * 33.4% = $1,350
PAMM accounts make trader’s life easier, offering a different approach to growing one’s wealth using the following features:
Automating trades by relying on an experienced FX money manager who makes investment decisions instead of the user.
Ensuring the money manager acts in good faith since they also trade with their funds in the same pool.
The ability to choose a suitable manager based on their trading system, record, risk tolerance and more.
A great option to diversify a trader’s portfolio and decrease the overall risks.
Managers can only access funds from the allocated pool, ensuring the safety of the trader’s account.
Despite the multiple advantages PAMM account trading brings, there are some downsides that traders need to consider.
The high fees of experienced money managers may offset the earned profits or minimise them significantly.
Positive returns are not guaranteed regardless of the manager’s experience. Financial markets may move unpredictably and result in losses.
Early withdrawal can be associated with penalties, which are variable based on the account manager’s choice.
Fast Fact
It is crucial to conduct due diligence in using PAMM accounts. Some fraud instances have been found utilising PAMM trading, offering unrealistic profit promises, excessive fees and too-good-to-be-true portfolios.
MAM accounts may look similar to PAMM in the concept of pooling funds together and assigning a money manager to execute market orders on traders’ behalf. However, MAM accounts provide more flexibility and access to original account holders.
This way, traders who entrust a manager in the MAM Forex account can customise their trading system, set up limits, adjust their risk tolerance level and more.
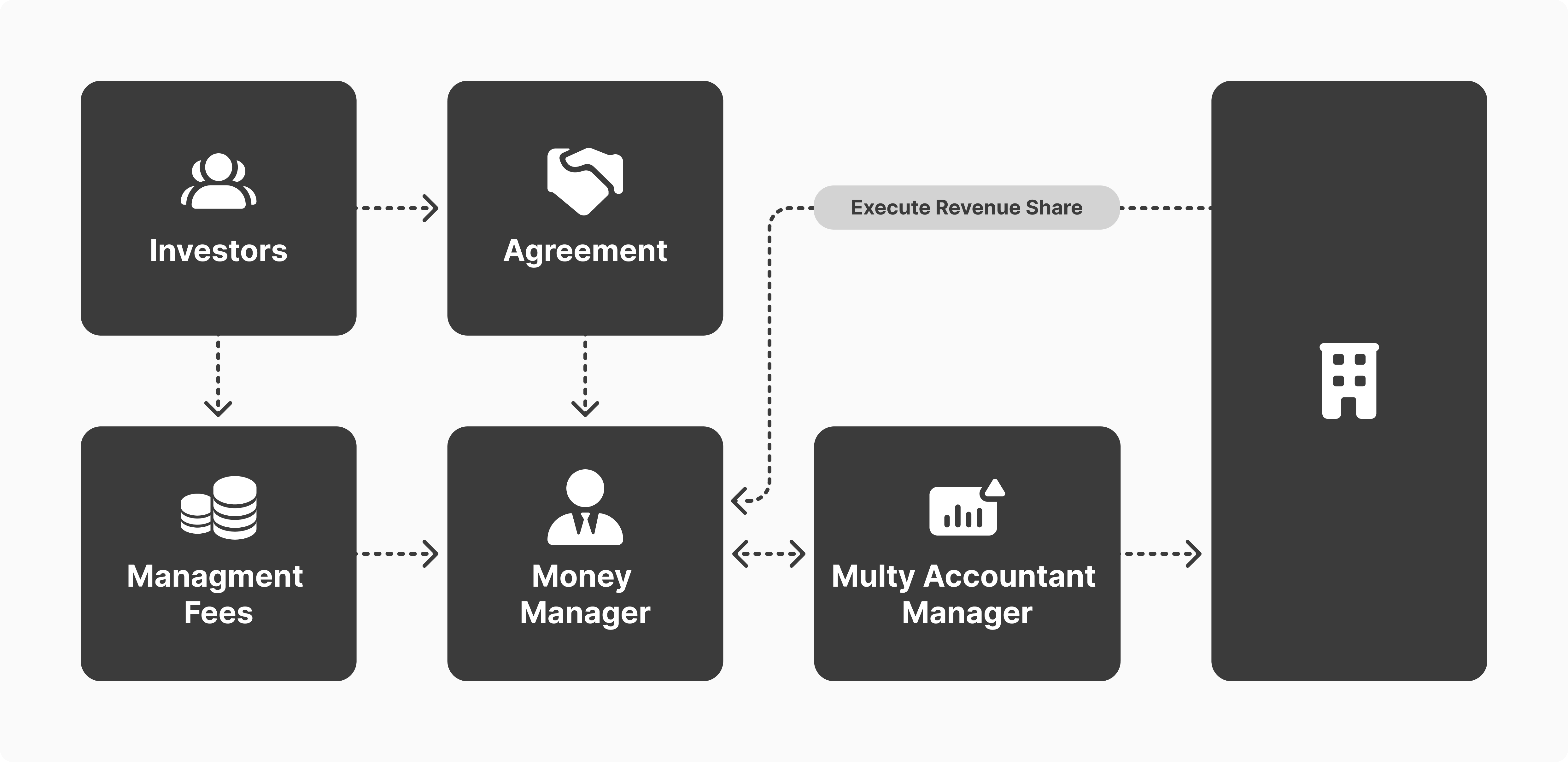
Trading with MAM accounts involves a master account and sub-accounts. The master account belongs to the money manager, who executes market orders, which are reflected in each sub-account.
Traders deposit their money in a shared pool funding each sub-account, where each trading decision made by the manager is replicated proportionally to each investor’s contribution.
The customisation feature sets MAM apart from other managed accounts. However, these options are limited by the master account’s owner, who decides on the type and level of freedom in these adjustments.
A professional trader can register with a Forex MAM broker to create a master account. Then, trading platform users can join FX MAM brokers using sub-accounts, which are all connected to the master account.
Let’s assume a MAM pool has five investors (5 sub-accounts) with a total of $50,000 invested by the traders. Say that the money manager is investing in Forex, trading EUR/USD and taking a position with 10 lots with the following distribution.
Jack = $5,000 (10%)
John = $8,000 (16%)
James = $10,000 (20%)
Thomas = $12,000 (24%)
Derek = $15,000 (30%)
As we mentioned, the master account is placing 10 lots, which are then distributed proportionally among the five traders as follows:
Jack = 10% * 10 = 1 lot
John = 16% * 10 = 1.6 lots
James = 20% * 10 = 2 lots
Thomas = 24% * 10 = 2.4 lots
Derek = 30% * 10 = 3 lots
The total must be 10 lots, and each trading decision the money manager makes in the market is reflected in each sub-account based on the number of lots invested in the market.
MAM money managers make their money through several fees, such as a performance fee, charged as a percentage of each trader’s profits. Other fees include a fixed managerial cost and volume fees.
Offering a MAM account on your brokerage platform is a smart way to attract more investors, especially newbies, who look to benefit from experts’ advice, as well as the following advantages.
Relying on experienced Forex traders, especially when a trader has a limited time to learn and wants to make it quicker to the market.
Minimising the conflict of interest since money managers are trading using their own accounts to grow their wealth.
MAM participants enjoy a high degree of flexibility in making adjustments to avoid losses or unbearable risks.
Opening a MAM account is an advanced way to diversify someone’s portfolio, where traders can invest and open multiple client accounts.

There are some downsides to using MAM accounts, and usually, traders make their choice by evaluating the advantages with the following disadvantages.
The full reliance on managed accounts can weaken the trader’s learning capacity and ability to analyse the market independently.
MAM managers’ fees can be relatively high, which could be around 30% of the earned profits.
Risk tolerance is usually different between an experienced money manager and a novice trader. Therefore exposing the sub-account to high risks.
Percentage allocation management module and multi-account manager accounts may look similar in how they offer managed trading using the experience of others. However, by explaining the details, you can find multiple similarities and differences.
Both accounts allow investors to rely on the knowledge of professional traders, usually with years of trading experience and know-how in the market and managed accounts.
Profits and losses are proportional to each trader’s investment and deposited money in the pool.
Money managers are expected to act in good faith because they trade for their accounts and are interested in accumulating profits for their own.
PAMM accounts provide little to no customisation for traders, with penalties for withdrawals or early departures from the pool. On the other hand, MAM accounts are more flexible, allowing sub-account owners to make changes and adjust their lot allocations or traded volumes, etc.
In PAMM accounts, money managers participate in the same pool with traders and share the resulting profits or losses. However, in MAM accounts, managers trade through their accounts and use their balance, and each step is reflected proportionally to each sub-account.
Withdrawing or depositing funds in PAMM accounts can only be done before or after each trading session, while MAM accounts allow participants to do so at any given time.
As the rule says, there is no one-size-fits-all as some prefer PAMM investor accounts while others want the flexibility of MAM trading Forex.
However, understanding your users and their needs helps you promote your business, demonstrating which account is more suitable for your users.
Traders who have a limited time to keep up with their accounts usually prefer this type, allowing them to capitalise on the knowledge and experience of market experts.
Inexperienced traders also prefer PAMM accounts since they don’t have sufficient knowledge yet to adjust their trading strategy or make alterations to their position.
Moreover, investors choose PAMM accounts to expand their positions in the market, diversify their asset classes and products, and minimise the risks associated with one market.
Experienced investors usually prefer MAM accounts, allowing them to take several market positions while enjoying control over their positions.
Investors use MAM FX accounts to automate their trading experience and expand their portfolios with the ability to make changes, add or withdraw funds and make decisions in a simple way.
PAMM and MAM accounts are two types of managed accounts that allow users to invest in financial markets through experienced traders, called money managers.
MAM accounts offer a higher level of freedom, allowing participants to adjust their traded lots and volumes, while PAMM accounts are locked in each trading session, and changes can only be made before or after.
MAM and PAMM Forex accounts entail multiple accounts pooling their money together, sharing the gains and losses as a percentage of their contributions. Therefore, these managed accounts are beneficial tools to attract more traders to your trading platform and grow your FX brokerage business.
PAMM and MAM include traders who deposit money in a shared pool and delegate a money manager to trade for them. MAM accounts allow participants to make changes to their market positions and trades, while PAMM accounts are locked in each trading session.
Traders enter a PAMM Forex account by depositing funds into a shared pool, which is traded by an experienced money manager, who makes investment decisions and executes trades on behalf of the participants.
PAMM account money managers can take risky trading positions that some participants cannot accommodate or have a limited budget. Also, just like any trading market, money managers can execute unsuccessful trades.
Multi-account manager trading involves traders who share a funded pool and choose a money manager who trades on their behalf. The manager uses a master account, and each decision is reflected in each participant’s sub-account.