CFD Trading Strategies: Why and How to Trade CFDs
 By Constantine Belov
By Constantine BelovAs a hard-working, goal-oriented, and well-rounded person, I always strive to do quality work for every job I do. Faced with challenging tasks in life, I have developed the habit of thinking rationally and creatively to solve problems, which not only helps me develop as a person, but also as a professional.
Speaking about my professional activities, I can say that I have always been attracted to the study of foreign languages, which later led me to the study of translation and linguistics. Having great experience as a translator in Russian, English and Spanish, as well as good knowledge in marketing and economy, I successfully mastered the art of copywriting, which became a solid foundation for writing articles in the spheres of Fintech, Financial markets and crypto.
 By Tamta Suladze
By Tamta SuladzeTamta is a content writer based in Georgia with five years of experience covering global financial and crypto markets for news outlets, blockchain companies, and crypto businesses. With a background in higher education and a personal interest in crypto investing, she specializes in breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand information for new crypto investors. Tamta's writing is both professional and relatable, ensuring her readers gain valuable insight and knowledge.

CFD trading is growing and maturing into an increasingly fashionable remedy for traders eager to profit from the price gains of financial liquids across global markets. Its unique flexibility allows traders to wager on booming and plunging markets without owning the asset.
This, combined with features like leverage and exposure to multifaceted markets such as stocks, FX, commodities, and indexes, makes CFD trading an appealing and versatile investment tool. However, the dynamic nature of CFDs requires a disciplined approach, clear strategies, and effective risk monitoring.
This article delves into the essence of CFD trading strategies, exploring their importance and the key components that define success. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding these strategies will provide the framework to navigate volatile markets, enhance decision-making, and achieve long-term trading goals.
CFD trading allows traders to profit from rising and falling markets, offering flexibility, leverage, and access to diverse global markets.
Developing a structured CFD trading strategy with clear entry and exit rules, risk surveillance, and market analysis is essential for consistent success.
Strategies like trend following, scalping, and news-based trading enable traders to adapt to market conditions and maximise opportunities effectively.
A CFD trading strategy is a structured and methodical approach that traders employ to “ride” on price moves in various financial markets using CFDs. Such a trading strategy outlines specific rules and guidelines for decision-making, including entry and exit points, risk enforcement measures, and trade sizing, ensuring a disciplined and analytical approach to trading.
The essence of a CFD trading strategy is aligning it with the trader's goals, risk tolerance, and market expertise. Strategies can range from short-term methods, such as scalping, which focuses on frequent, small profits, to longer-term approaches, like trend following, which capitalises on sustained market movements.
CFD trading strategies are particularly valuable because they provide a structured framework for navigating volatile and unpredictable markets. By following a predefined plan, traders can mitigate emotional decision-making and improve consistency in their performance.
Furthermore, the flexibility of CFDs, which allows trading in both rising and falling markets, offers opportunities for traders to adapt their strategies to various market conditions.
This adaptability, rigorous risk oversight, and continuous strategy refinement form the foundation for sustainable success in CFD trading.
Fast Fact
Unlike futures contracts, CFDs typically don’t have an expiration date.
A CFD trading strategy is a comprehensive plan that includes specific elements to guide traders in achieving consistent results while managing risks effectively. Below are the key components that form the foundation of a successful CFD trading strategy:
The first step is choosing the financial markets or instruments to trade. This involves understanding the characteristics of different markets, such as trading hours, liquidity, and volatility. Traders should focus on markets that align with their expertise, preferences, and goals.
A solid strategy relies on a clear framework for analysing and predicting market movements. This includes studying price trends and patterns, evaluating market fundamentals, and assessing overall market sentiment. Combining these analytical approaches can provide a deeper understanding of potential trading opportunities.
Managing risk is a critical part of any CFD trading strategy. This involves setting limits on how much capital to risk on a single trade, using tools like stop-loss orders to limit losses, and defining profit-taking levels to secure gains. A well-structured risk mitigation plan ensures that losses are controlled and trading remains sustainable.
A successful strategy includes clear criteria for entering and exiting trades. Entry rules specify when to open a position based on market conditions or indicators. Exit rules define when to close a trade to capture profits or minimise losses. Following predefined rules helps maintain discipline and consistency.
CFDs are leveraged products, so managing leverage is essential to minimise financial risks. This involves using leverage levels that align with your risk tolerance and ensuring that your positions remain manageable under different market conditions.
The strategy should reflect the trader’s preferred style and timeframe. Depending on personal preferences and availability, the trader can choose to focus on short-term or long-term trading. Aligning the strategy with one's lifestyle ensures it is practical and effective.
Markets are constantly changing, so monitoring trades and market conditions is crucial. Reviewing and adjusting the strategy based on performance and evolving trends helps maintain its effectiveness and ensures long-term success.
A disciplined approach to trading is essential. This means sticking to the strategy, avoiding impulsive decisions, and managing emotions like fear or greed. Emotional control helps traders remain consistent and objective in their decision-making.
Backtesting the strategy on historical data helps evaluate its reliability and effectiveness. Regularly reviewing and refining the strategy ensures that it adapts to changing market conditions and remains a viable tool for achieving trading goals.
Trading CFDs offers unique advantages that appeal to both beginner and experienced traders. Here are the primary reasons to consider trading CFDs:
CFDs encourage market participants to operate larger positions with less equity. This use of leverage can increase potential returns by requiring only a fraction of the total trade value upfront, enabling traders to use their funds more efficiently.
With CFDs, traders can speculate on price movements in both directions. Going long (buying) allows for profit when prices rise, while going short (selling) allows for profit when prices fall. This flexibility is a key advantage of CFD trading.
CFDs provide access to a wide range of financial markets, including stocks, forex, commodities, indices, and cryptos. This enables traders to diversify their portfolios and take advantage of opportunities across multiple asset classes.
CFD trading involves speculating on price movements rather than owning the underlying asset. This eliminates the complexities and costs associated with physical ownership, such as storage fees for commodities or transfer fees for stocks.
CFDs often have lower transaction costs compared to traditional trading methods. Many brokers offer tight spreads, and there are usually no commissions or stamp duty fees in certain jurisdictions. This makes CFDs an attractive option for cost-conscious traders.
CFDs can be used as a hedging tool to offset risks in an existing portfolio. For example, traders can execute short CFD positions to protect against potential losses in their long-term investments during a market downturn.
CFD brokers typically provide advanced trading platforms equipped with real-time data, charting tools, technical indicators, and risk prevention features. These tools enhance decision-making and allow traders to execute strategies effectively.
CFD trading often offers extended market hours, especially for Forex, indices, and cryptocurrencies. This flexibility allows traders to respond to global events and trade outside traditional market hours.
Unlike futures contracts, most CFDs do not have a fixed expiration date. This allows traders to hold positions for as long as desired, subject to overnight financing costs, offering greater flexibility in managing trades.
CFDs thrive in volatile markets, where frequent price movements create opportunities for traders to profit. Active traders can use well-timed strategies to benefit from the dynamic nature of markets.
CFD trading platforms provide easy access to global markets with minimal capital requirements. With online platforms and mobile apps, traders can manage their positions anytime and anywhere, ensuring convenience and accessibility.
CFD trading involves speculating on the price fluctuations of various financial assets, such as stocks, Forex, commodities, or indices, without owning the underlying asset. Here’s a step-by-step guide to trading CFDs:
CFDs are financial instruments that allow you to profit from both rising and falling markets. If you expect the price of an asset to rise, you can go long (buy). If you believe the price will fall, you can go short (sell).
CFDs also involve leverage, meaning you can take over a larger stake with a smaller initial investment. However, leverage amplifies potential gains and losses, so it’s crucial to use it responsibly.
Choose a broker that provides access to various markets and offers a user-friendly platform with tools for analysis and execution. Ensure the broker is regulated, transparent about fees, and provides adequate customer support.
Register with your selected broker and complete the account verification process. Deposit funds into your trading CFD account using your preferred method. Most brokers require a minimum deposit, which can vary.
Conduct market analysis to make good trading picks. Use technical analysis to study price charts and patterns, identifying trends and potential price levels. Use fundamental analysis to assess economic data, company performance, or other factors affecting the asset. You can also consider market sentiment analysis to gauge the overall mood and direction of the market.
Based on your analysis, determine whether to go long or short. Set the position size and leverage level you are comfortable with, considering your risk tolerance and account size. Establish your entry point and stop-loss and take-profit levels to manage your risk.
Enter the trade through your broker’s platform, specifying the asset, position size, and risk oversight settings, such as stop-loss or take-profit orders. Confirm the trade and monitor its progress.
Track the performance of your open positions. Use real-time charts and market data to stay updated. If market conditions change, you may need to adjust your stop-loss or take-profit levels to protect your capital or secure profits.
Close the trade manually when you believe the time is right, or let it close automatically when your stop-loss or take-profit levels are triggered. The difference between the opening and closing prices determines your profit or loss.
After closing the trade, review its outcome and assess what went well and what could be improved. Regularly refining your trading strategy based on your experiences and market conditions is key to long-term success.
A solid CFD trading strategy helps traders make deliberate decisions, maximise opportunities, and manage risks effectively. Below are some of the most commonly used and effective strategies:
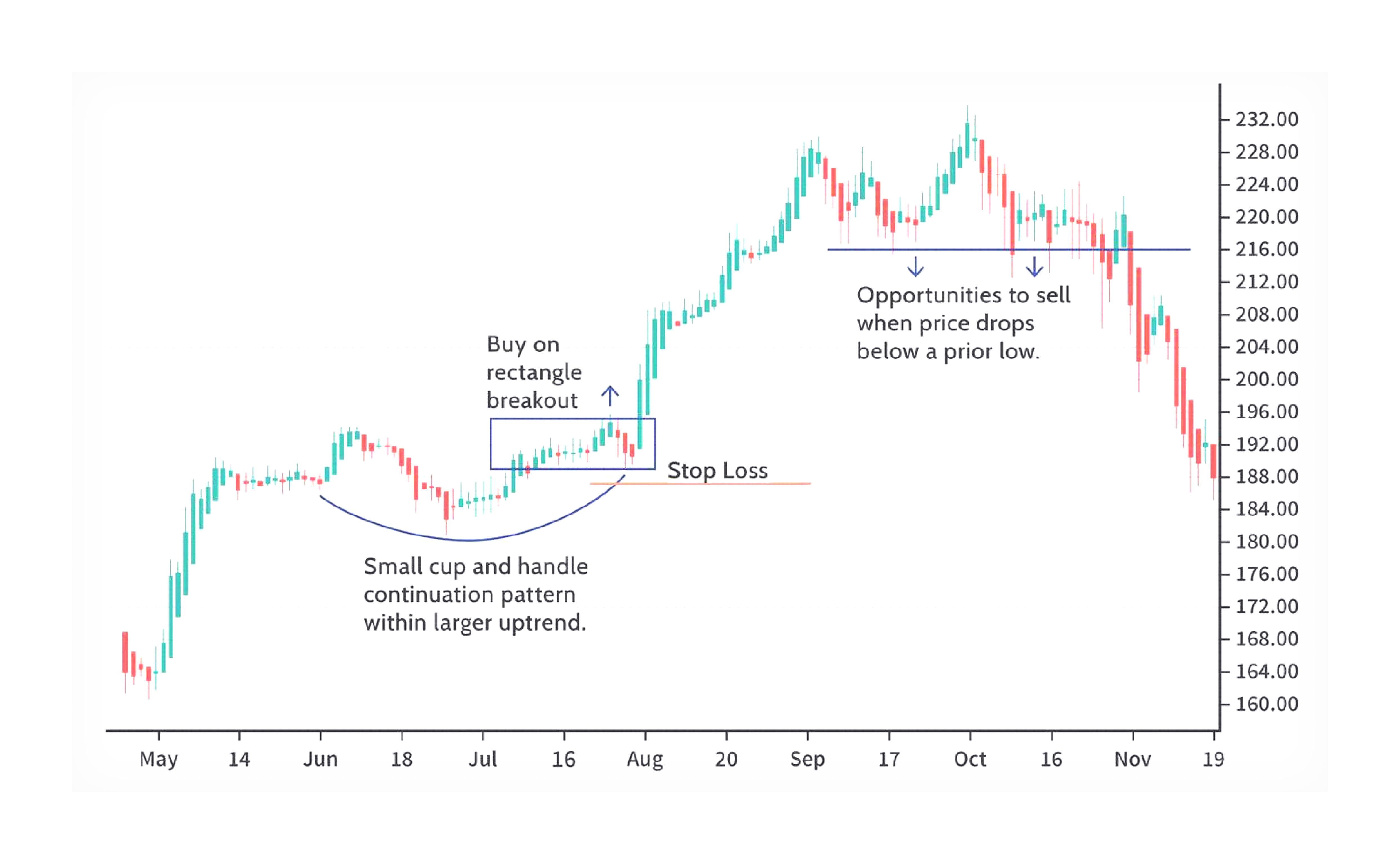
This strategy focuses on identifying and trading toward a prevailing market trend. Traders aim to capitalise on sustained price surges by using technical tools to confirm the trend's strength and direction. This strategy works best in markets where price trends are consistently upward or downward over a period of time.
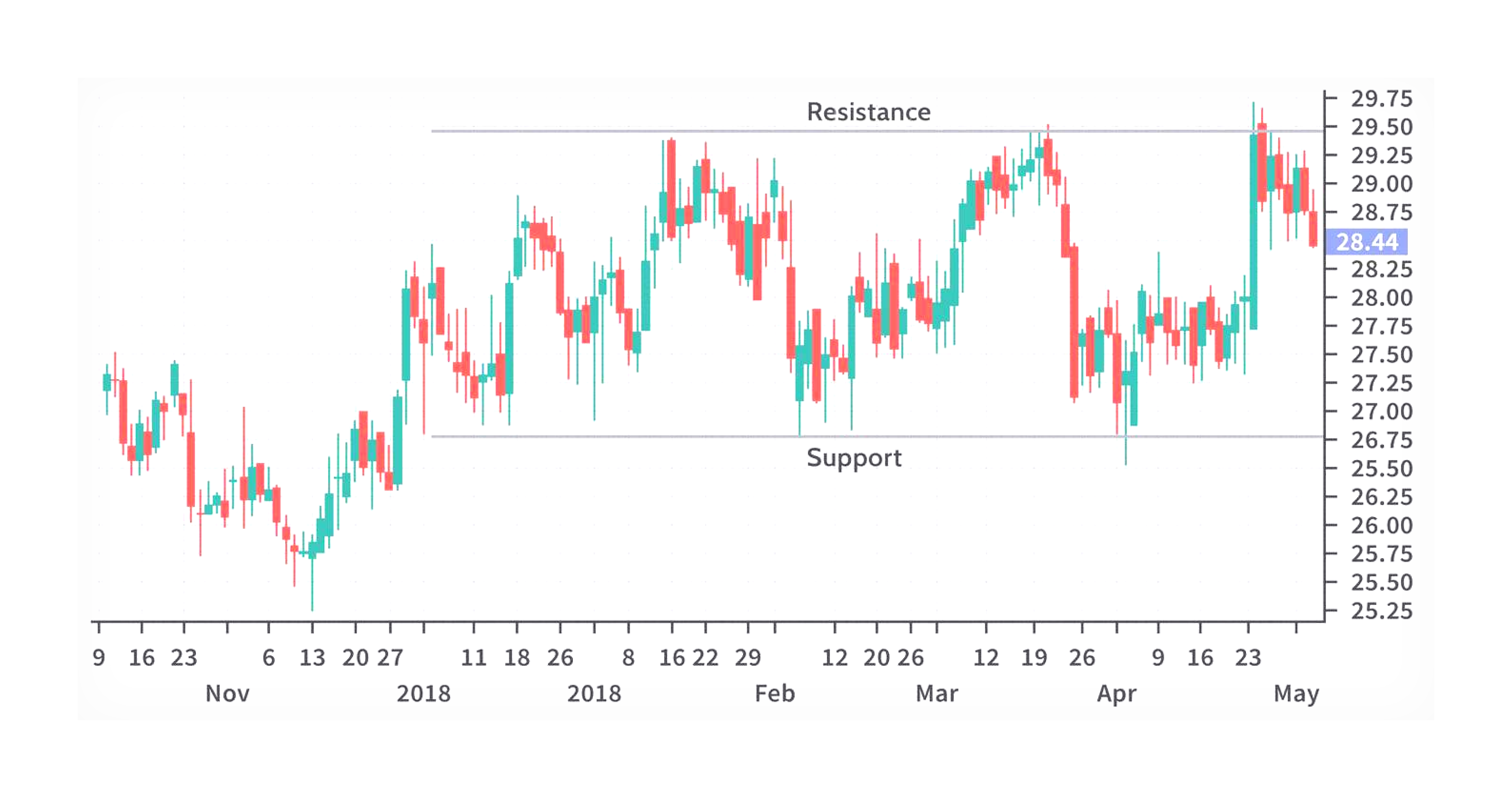
Range trading involves identifying price levels where an asset consistently moves within a certain range, bounded by support (the lower boundary) and resistance (the upper boundary). Traders aim to profit from price fluctuations between these levels by buying near support and selling near resistance. It is typically used in markets that lack a clear trend.
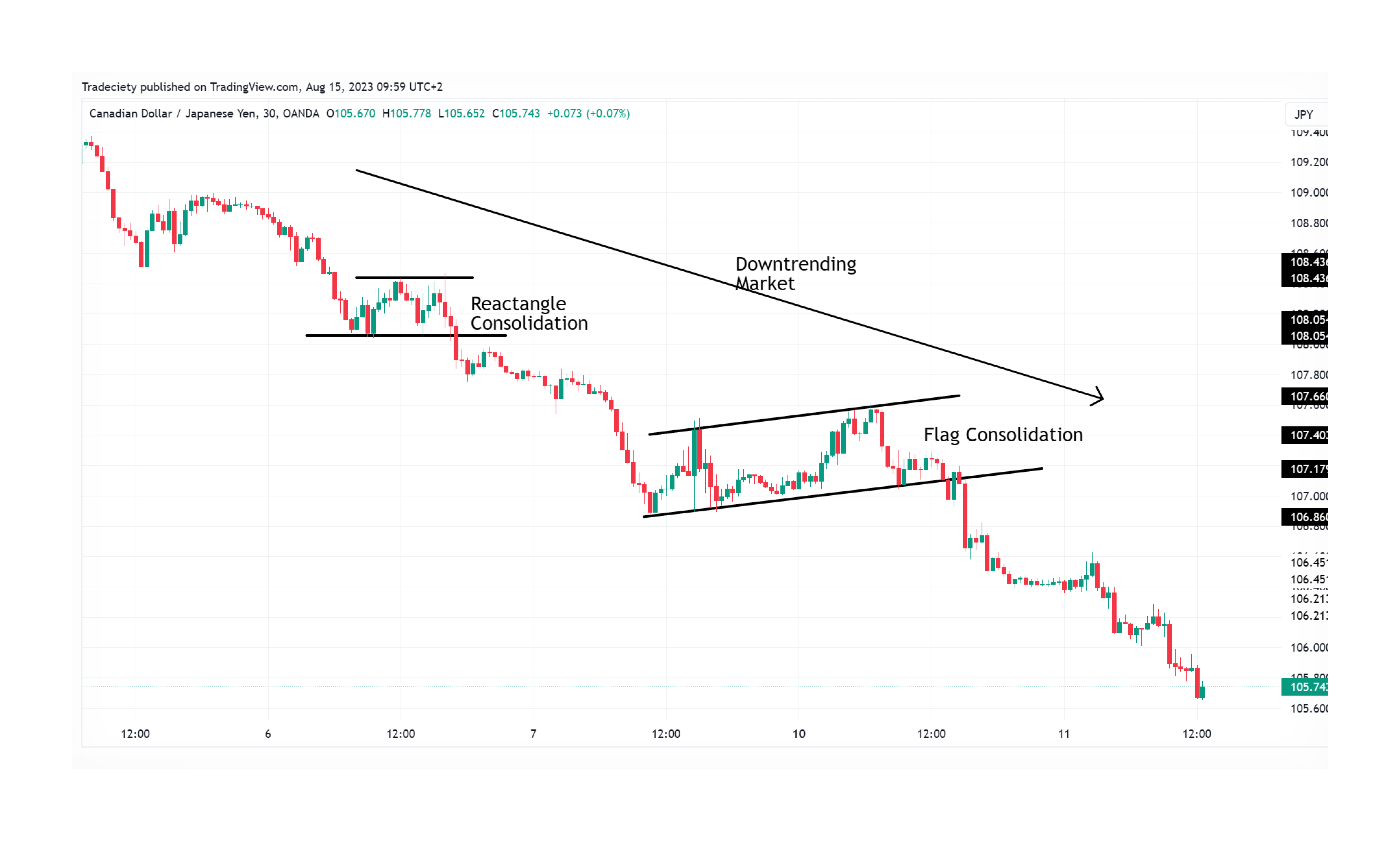
Breakout trading capitalises on price swings when an asset breaks through a significant support or resistance level. These breakouts often signal the start of increased volatility and the potential establishment of a new trend. Traders use this strategy to enter the market early during these shifts.
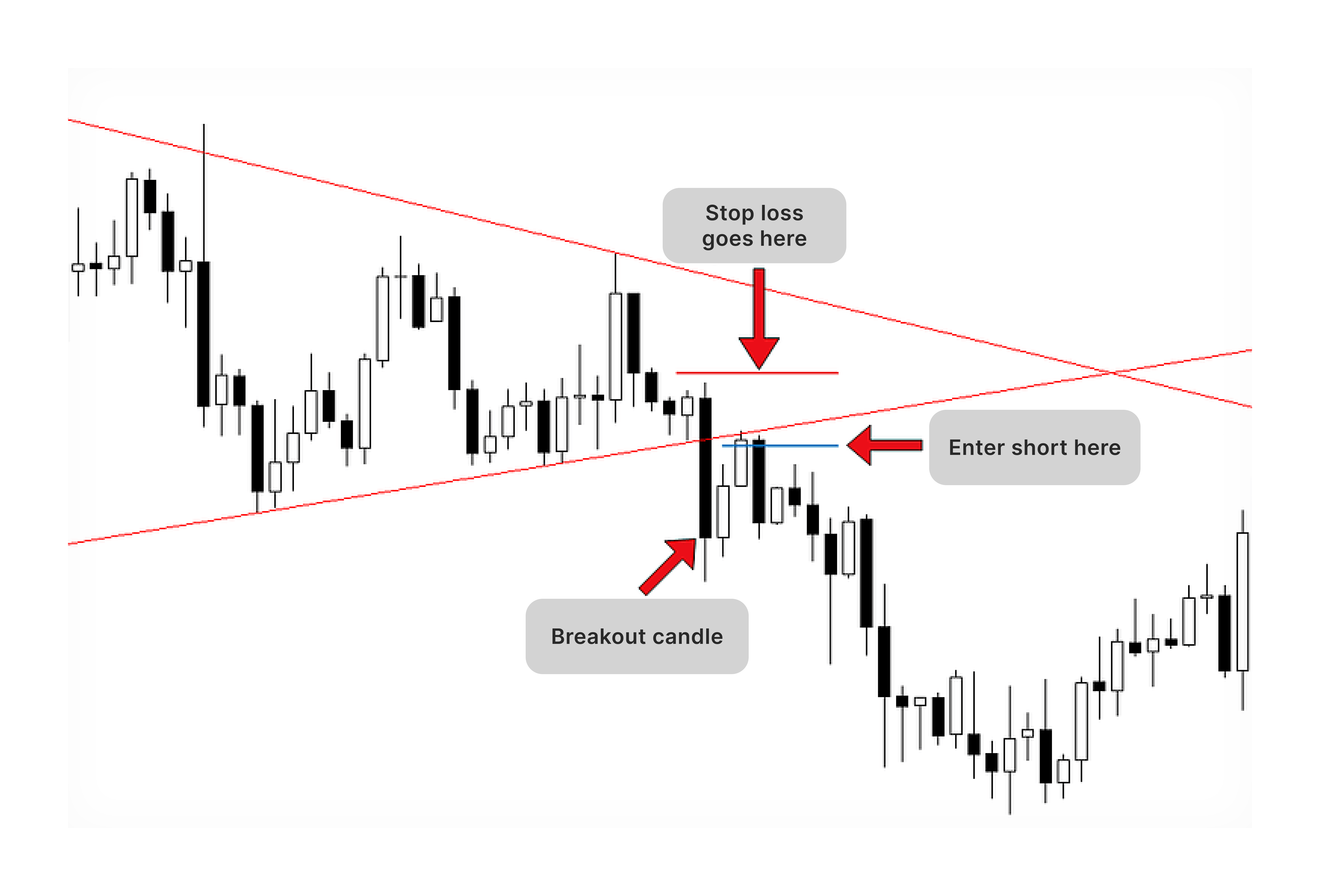
This strategy involves holding positions for several days or weeks to capture short- to medium-term price drops. Traders aim to profit from price "swings" as the market moves upward or downward, relying on technical analysis to time entries and exits. This approach is suited to traders who prefer a balanced timeframe.
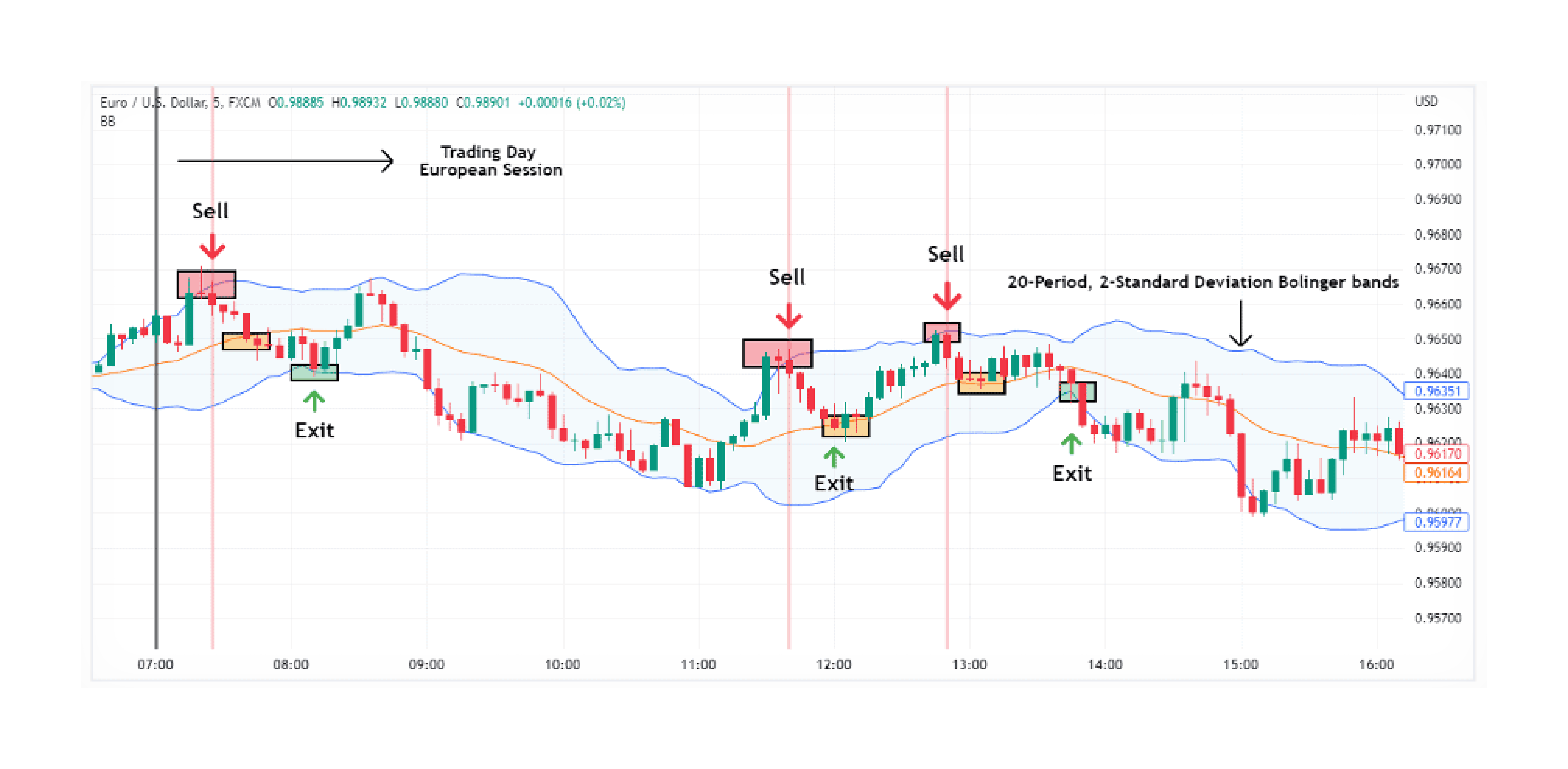
Scalping is a short-term strategy that focuses on making small profits from frequent trades. It requires traders to act quickly on minor price fluctuations, closing positions as soon as a profit is achieved. This strategy demands precise execution and is generally used in highly liquid markets.
CFD trading offers unmatched flexibility and opportunities, enabling traders to profit from various financial markets in any market condition. However, success in CFD trading hinges on adopting a well-defined strategy that aligns with personal goals, risk tolerance, and market expertise.
By integrating key components such as market analysis, risk handling, and emotional discipline into their approach, traders can develop a structured framework to navigate the complexities of CFD trading. With a solid foundation and disciplined execution, CFD trading can be a powerful tool for achieving consistent and sustainable financial growth.
CFDs are financial tools that allow you to trade on the price patterns of assets like stocks, forex, and commodities without owning them.
CFDs offer the flexibility to generate income from bullish and bearish markets, access to various global markets, and the ability to trade with leverage.
Popular strategies include trend following, range trading, breakout trading, scalping, and news-based trading. Each strategy is suited to specific market conditions.
Choose a regulated broker, learn market analysis, develop a methodology, pull off risks with stop-loss triggers, and monitor your trades consistently.