Advantages of Long Term Stocks: Does HODLing Pay Off?
 By Otar Topuria
By Otar TopuriaOtar is a seasoned content writer with over five years of experience in the finance and technology niche. The best advice he received was to read, which has led him to an academic background in journalism and, ultimately, to content writing. He believes everything can be brought to life through words, from the simplest idea to the most complex innovation.
 By Tamta Suladze
By Tamta SuladzeTamta is a content writer based in Georgia with five years of experience covering global financial and crypto markets for news outlets, blockchain companies, and crypto businesses. With a background in higher education and a personal interest in crypto investing, she specializes in breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand information for new crypto investors. Tamta's writing is both professional and relatable, ensuring her readers gain valuable insight and knowledge.

Individuals who are carefully planning their futures often choose to invest in long-term stocks. This involves buying and holding stocks for a long time to reap the benefits of steady growth and profits.
Investors value consistent price rises, dividend payments, and the ability to deal with brief market turbulence.
This article stresses the importance of an investment plan and examines the extended benefits of owning stocks, such as tax advantages, lower market risk, and steady income flow.
Stock investing typically refers to stable growth, capital appreciation, and tax efficiency over a period of five to ten years or even more.
After some time, individuals gain from compounding returns and dividend reinvestment, which raise the value of investments.
Long-term investors can endure volatility by concentrating on stable increases rather than periodic price swings.
When an individual decides to buy and hold stocks for a long time, usually five to ten years or more, this is a long-term stock investment.
This strategy prioritises consistent growth over time to achieve capital appreciation, compounding returns, and tax efficiency. It differs from short-term trading, which centres on frequent purchases and sales to profit from transient price swings.
Disciplined decision-making and patience are critical components of extended investment plans. In contrast to short-term trading, investors profit from remaining invested during short-term market volatility, which requires active management to react to fleeting market fluctuations.
Reducing the influence of transient price changes caused by internal or external factors enables stock prices to more precisely reflect a company's growth and general industry trends.
Investors pay attention to dividends, which can be a reliable source of income from equities that pay dividends regularly. Tax advantages, such as reduced rates on capital gains relative to short-term profits, further encourage long-term investments.
Investors value a company's potential over daily price fluctuations by holding stocks through market risk and short market swings. This strategy takes advantage of the stock market's sustained expansion, guaranteeing steady cash flow and robust profit margins that support significant growth over time.
The question is, why is it beneficial to invest over a long period of time? Let's say you wanted to save money, and instead of saving it, you decided to invest in Nvidia's stocks.
Nvidia produces high-tech semiconductors in phones, computers, AI, and other devices. When Nvidia went public in 1999, its stock price soared! Here's the deal:
You invested $10,000 in Nvidia (NVDA) in 1999.
Since then, the company has grown approximately 322,185% over 30 years.
The current value of your $10,000 investment would be $32,228,453.
Here are some of the other best long term stocks (August 1994 - July 2024):
Amazon.com Inc. (AMZN): return of 249,208%
Monster Beverage Corp. (MNST): 164,539% return
NVR Inc. (NVR): return of 140,431%
Apple Inc. (AAPL): return of 88,807%
Long-term growth in the stock market has typically been fuelled by growing economies and inflation, which raises asset values gradually. Even in brief disruptions, investing enables people to profit from the market's long-term growth.
Stock prices frequently change in response to both internal and external causes, including economic data, earnings reports, and geopolitical events. During these transitory market swings, patience allows investors to stay invested and avoid making quick judgements based on temporary price changes.
Historical evidence supports the benefits of this approach. Despite short-term volatility, the S&P 500 has historically produced an average yearly return of roughly 9–10% over long periods of time. Longer investment duration can mitigate losses from prolonged downturns, as evidenced by the Dow Jones Industrial Average's significant increase over decades.
Instead of focusing on daily price fluctuations, investors consider steady profit growth, robust profit margins, and a company's continuous expansion. With this strategy, they can profit from dividend growth, long-term capital gains tax advantages, and consistent price increases—all advantages of stock ownership.
Another benefit of extended investing is compounding returns. Reinvested dividends from dividend-paying companies support compound growth and consistent income sources. This steady income flow, through steady increases over time, helps reach financial objectives and fortify a sound economic basis.
Reinvesting earnings or dividends has a compounding impact that increases returns over time. Every dividend or gain that is reinvested expands the investment base, enabling future earnings to grow more significantly.
Take a $1,000 starting investment with a 10% yearly compound return, for instance. After a year, the investment increases to $1,100. The second year's return is computed at $1,100, which comes to $1,210 after reinvesting the $100 gain. Over the course of five years, the investment increases to about $1,611, illustrating the compounding effect of exponential growth.
The compounding effect intensifies with the length of time an investor invests. Long-term strategy-takers are rewarded, and their portfolios can increase steadily despite short-term market swings.
Compounding offers substantial advantages for investors committed to reaching their financial objectives. This benefit is further enhanced by dividend-paying stocks that pay dividends regularly since reinvested dividends support a stable cash flow and income source.
Compounding can provide growth for long-term holdings that exploit a company's competitive edge and steady expansion. Reinvesting earnings, steady earnings growth, and excellent profit margins create a strong financial foundation for significant growth over time.
Because short-term drops in stock prices often have less of an effect over time, this method also helps investors weather economic downturns. Investors can maximise their gains by staying invested and concentrating on the market's long-term growth, allowing them to profit from both capital appreciation and dividend increase.
Short-term price fluctuations frequently reflect internal or external variables that momentarily impact stock values. As a solid financial foundation suggests, it is built through constant earnings growth and stable price appreciation. These short-term market fluctuations lose significance over time.
Instead of responding to daily price fluctuations, long-term investors concentrate on a company's consistent growth. Thanks to this technique, investors can hold onto their investments during times of market turbulence.
For instance, the Dow Jones Industrial Average fell precipitously during the 2008 financial crisis. When the market as a whole rebounded during the next ten years, investors who kept their portfolios intact saw significant growth.
In 2020, the impact of COVID-19 on the market led to a prolonged decline in numerous industries. Nevertheless, extended stock investments in businesses with steady cash flow and competitive advantages recovered once markets stabilised. These illustrations demonstrate the benefits of stock ownership during recessions.
Long-term investing lowers the risks involved with short-term ones. Investors gain from broader sector trends and the capacity to withstand economic downturns, but short-term gains frequently depend on timing quick market movements. When the whole market recovers and expands, time usually results in more capital appreciation.
Because markets have traditionally produced long-term growth, dividend-paying companies are appealing to investors looking for reliable sources of income. By combining tax advantages with growth potential, dividend reinvestment aids investors in reaching their financial objectives. Unlike short-term gains, holding investments for more than a year reduces tax obligations.
By embracing this approach, investors can create a strong financial foundation that sustains steady cash flow and healthy profit margins.
Using the dollar-cost averaging approach, investors set aside a certain sum of money regularly to buy the same stock or other securities at any given price. This approach minimises the risks involved in trying to time the market and guarantees steady investment contributions over a long period of time, lessening the impact of brief swings.
This approach evens out the total cost of investing by buying shares at both high and low market prices. For instance, investors purchase additional shares for the same set price if stock prices momentarily drop due to internal or external circumstances. On the other hand, when stock prices rise, fewer shares are bought. This strategy reduces the average cost per share over a longer time frame.
Historical data demonstrate the benefits of investing in stocks. Take an investor who makes $100 monthly for five months, for example. The average cost per share may be substantially less than regularly buying at the highest price if share prices range between $2 and $5 during this period. This technique promotes consistent price growth by eliminating the emotive choices involved in market timing.
Dollar-cost averaging supports consistent contributions to investment portfolios, which is consistent with broader industry trends. Concentrating on long-term growth potential rather than responding to transient market swings or short-term changes produces growth for the future.
Long-term investing with dollar-cost averaging produces steady cash flow, a solid financial base, and less influence from daily price fluctuations. This approach is frequently used by 401(k) accounts and dividend reinvestment plans to assist investors in reaching their financial objectives and providing consistent income.
Additionally, this method has tax advantages in case investments are kept for more than a year. In contrast to short-term volatility, investors concentrate on a company's potential by adhering to a regular investing schedule. Over an extended period, this method maintains a diversified portfolio, healthy profit margins, and consistent income streams.
Fast Fact
Based on a trading volume of 663,287 shares, GeneDx Holdings Corp. (WGS) has experienced impressive growth of 4,897.52% in less than a year. Its stock price is $80.46, and its market capitalisation is $2.21 billion.
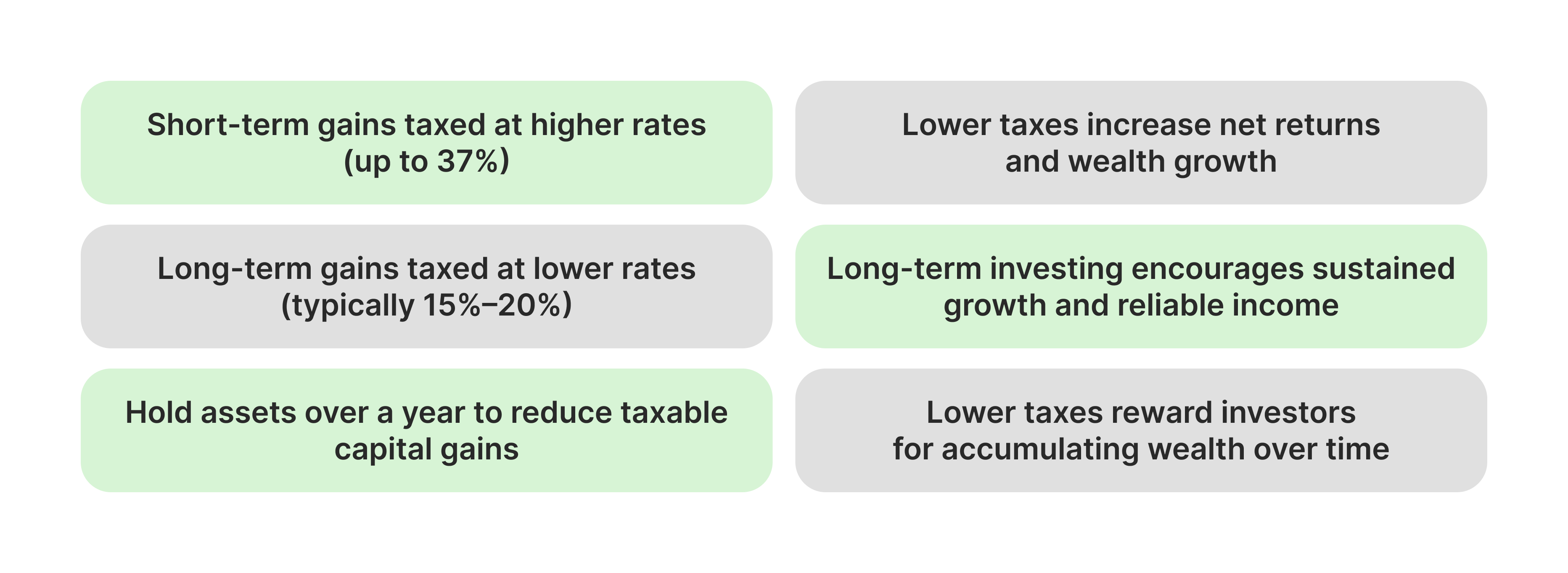
When an asset is sold for more than it was initially purchased for, capital gains tax is due. This tax varies depending on the length of time held before sale, and it applies to investments such as stocks.
Assets held for a year or less are subject to short-term capital gains, which are subject to higher ordinary income tax rates—up to 37%. Conversely, assets kept for over a year are subject to long-term capital gains, which are taxed at much lower rates—typically 15% or 20%, depending on income.
A 50% reduction in taxable capital gains is offered to investors who hold equities for more than a year, enabling them to keep a larger portion of their profits. Since it increases net returns over time, this tax benefit is a significant incentive for extended investing.
Investors can multiply their wealth by reinvesting more gains when they pay less in taxes. Also, investments for the future have preferential tax treatment over short-term transactions, where higher tax rates might reduce profits.
Reduced capital gains Long-term investors are rewarded by taxes, which enable them to retain a more significant portion of their profits. This is a massive advantage for people interested in accumulating wealth over time.
Since long-term holders enjoy lower taxes and the chance for sustained price appreciation and reliable income flow, the tax treatment also encourages investing in businesses with significant, sustainable growth potential.
Long-term investing allows investors to allocate investments across several industries and geographical areas. By distributing their assets across various industries and geographical areas, investors can lower their exposure to the risks associated with any market segment or region. This diversity lessens the effect of swings caused by external or internal variables that could temporarily affect stock prices.
Diversified portfolios can profit from various trends and seize chances in diverse markets. Diverse assets offer exposure to industries with steady earnings growth, competitive advantages, and businesses with growth potential, even when market conditions change.
Investing in expanding and stable industries increases a portfolio's robustness. The stocks of these industries often offer constant cash flow, sustainable price growth, and the possibility of regular dividend payments.
Even during prolonged downturns or brief swings, these investments contribute to the long-term maintenance of a strong financial base and steady revenue streams. These consistent returns benefit investors, who are better equipped to handle daily market fluctuations and reach their financial objectives.
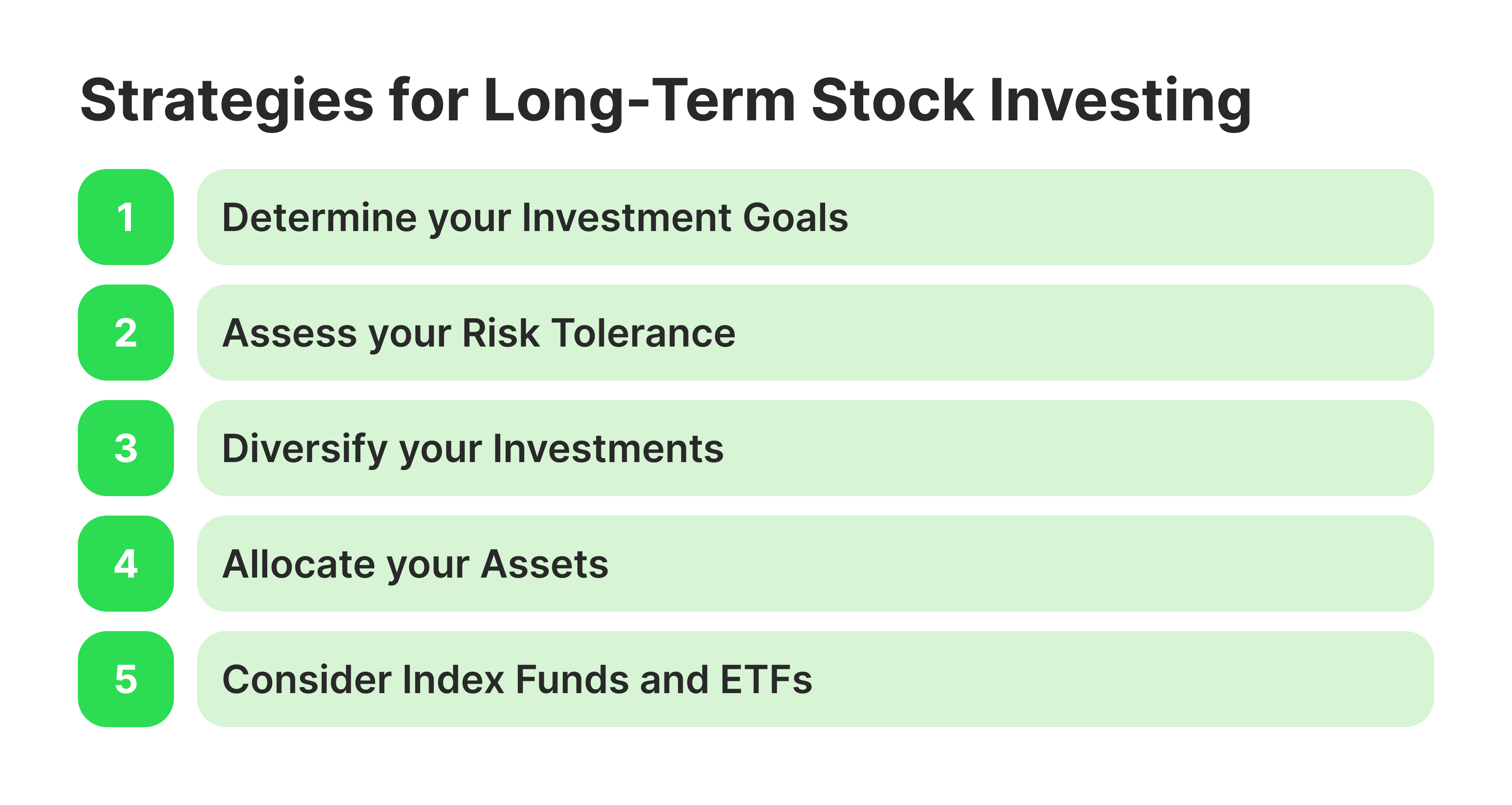
Making the most of long-term stock purchases requires careful execution and strategic planning. The following tips can help brokers and traders succeed in the long run.
Clear financial objectives with precise deadlines form the foundation of an organised investment strategy. Establish goals and ascertain the anticipated time frame for achieving them. A clear path improves focus and direction, although adjustments can be made over time.
Invest in businesses with a history of producing sustained price appreciation, a competitive edge, and continuous earnings growth. High-quality stocks are more resilient to short-term swings and exhibit consistent growth.
To take advantage of compounding, reinvest dividends from equities that pay dividends regularly. Using the power of reinvestment can improve portfolio growth and guarantee a consistent income stream over time.
Examine your portfolio frequently to make sure it supports your objectives, but refrain from making pointless trades. Profits can be reduced by overtrading, particularly during short fluctuations. The goal of consistent investing is to persevere through market cycles.
Stay informed on economic developments, financial news, and market trends that could have a short-term impact on stock prices. Understanding the internal or external forces influencing stock market fluctuations enables investors to concentrate on the company's core values and make decisions that will help them reach their financial objectives.
Distribute risk among sectors, industries, and geographical areas to lessen exposure to a particular asset class. While reducing the risks connected with individual investments, broad diversification guarantees that investors profit from market development as a whole.
Pay attention to long term stocks with consistent cash flow. Stable revenue from businesses with solid financials and stable earnings growth usually supports long-term investment strategies and maintains stability amid market downturns.
ETFs and inexpensive index funds provide broad market exposure with low costs. Cutting expenses over time can yield significant savings, which will support the expansion of the portfolio as a whole.
Tax-efficient investments can improve returns, such as using tax-deferred or tax-free accounts. The growth of long-term investments can be further enhanced by maximising tax benefits through schemes such as Roth IRAs.
Understanding the inherent risks is essential, even if long investing tends to lessen the impact of short market swings. Since markets tend to trend upward over longer periods of time, holding onto investments throughout prolonged downturns might result in recovery and growth.
Holding stocks offers investors consistent gains, tax savings, and less market risk. Compounding returns, a consistent income source, and capital appreciation are also advantages.
This technique, which requires patience and discipline, allows individuals to ride out short-term volatility and concentrate on future rewards. Investment holdings allow individuals to build wealth and lessen their exposure to market swings, eventually helping them achieve their financial objectives.
Long-term investors disregard short market swings in favour of concentrating on a company's potential for growth. Over time, they place a high priority on strong financial principles like income and profit.
Compared to other investing options, long-term stock holdings provide the possibility of capital growth and higher returns. Additionally, it offers dividends as a passive source of income.
Stocks held for more than a year can be eligible for a lower capital gains tax rate, which could result in fewer taxes. Higher earners may save up to 17% over regular income tax rates, while investors in lower tax categories may pay nothing on their gains.